Selection of Wear Coatings and Treatments for Maximum Achievable Reliability of Motor Spindles and Bearings
The selection of the proper coatings and treatments to be used for a wear resistant job is the most important step in doing the job successfully. Each wear coating has different characteristics of strength, shrinkage, hardness, and other qualities, such that there is a material for every wear resistant category. There are two general material approaches to wear resistance. Firstly, wear resistant material can be used as a material that resists wear by virtue of its composition or its properties. Secondly, as a structural part material that can be used, while its surface is modified by treatments and coatings to provide the desired level of wear protection. A cost-effective selection of the desired surface quality and reliability is possible with the combination of the two methods for achieving maximum wear resistance, while using integrated multivariate reliability sensor-based selection device (IMRSSD).
A wide variety of treatments and coatings have been developed using different coating techniques and methods of application. These coatings and treatments fall under the following three categories:
– Soft Coatings or Solid Film Lubricants: These coatings provide protection by preventing adhesion between the substrates. Since they have low shear strength, they shear in preference to the substrate giving a low friction coefficient. The coating will also flow to better distribute the contact area, which promotes increased load and temperature capacity.
– Surface Treatments: Surface treatments modify the surface either to make it harder or to provide a more wear resistant alloy at the surface. Generally, these treatments increase the surface hardness and provide wear resistance by virtue of that increase.
– Hard Surface Replacement Coatings (Hard Surfacing): These types of coatings do not modify the existing surface but replace it with another surface. In this case, the wear behavior is only a function of the coating and not the base material. Examples of such coatings are chrome plate and weld overlays. Sprayed carbide and ceramics are also included in this category.
Hard Surfacing Category can easily be controlled by an engineering technique to achieve a maximum reliability, since a desired controlled surface can be derived mechanically. Hard surfacing is a process by which an alloy coating is welded, fused, or sprayed onto a critical area of a metal part. Although the name implies a wear resistant coating, hard surfacing is undertaken to provide a variety of desired properties including wear resistance, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and strength. At this point, it is worth mentioning that, there are two kinds of hard-surfacing namely hard-facing and spray coatings. Hard facing is applied by using welding techniques which assures a metallurgical bond, while spraying is accomplished by impinging the substrate with high velocity powder. Bonding in this case is usually mechanical. Spraying applies the coating which is up to 0.050 cm.
The two general uses for hard surfacing are that, it can be applied to repair worn surfaces, and can be applied to obtain more desirable surface properties. Hard surfacing competes with surface treatments and soft coatings and should be given equal consideration in the design of mechanical machine parts like motor spindles and bearings. Irrespective of the range of coating properties, the advantages of hard surfacing are the greater the thickness available the better it is to achieve maximum quality and reliability.
Selecting the best wear resistant material properties, coated surface quality and reliability with integrated multivariate reliability sensor-based selection device (IMRSSD)
The technique can be used to determine the criticality, priority and category of properties, components, and systems. It is therefore used for selection, comparison and recommendations in companies and organizations. This can be done with the help of an integrated multivariate reliability sensor-based selection device (IMRSSD) [1] and a real-time measurement of wear-resistant materials (Fig.1)
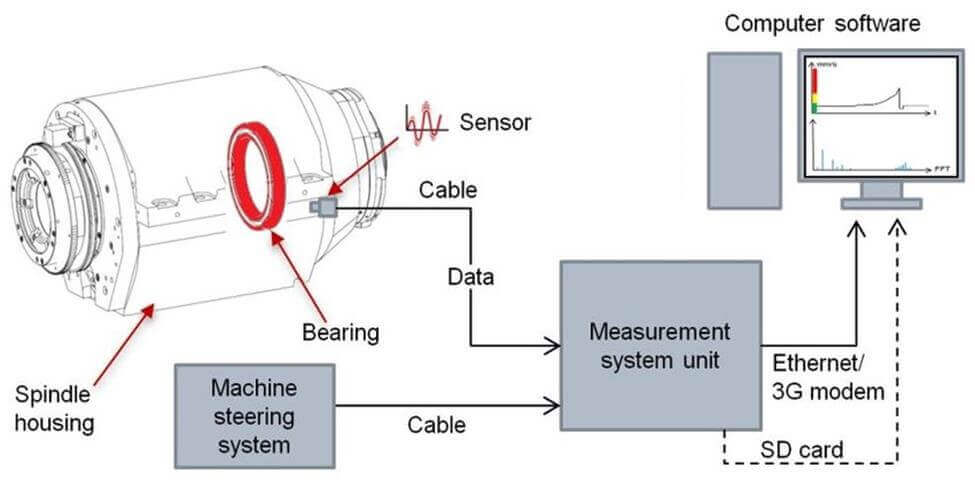
Figure 1. A Typical Real-Time Measuring Device for the Selection of Wear Resistance Coating Materials
Benefits of IMRSSD
- IMRSSD is used to select the desired categories, property requirements for treatment of wear and corrosion resistant materials and hard-coating processes
- It is used to determine the criticality and priority of wear/corrosion resistant materials.
- It used to select piezoelectric materials and conditions for the design of piezoelectric sensors and for the determination of natural frequency of a motor spindle.
- It is used in the design of experiment to acquire a hard-turning machining process and coated spindle signals from the integrated multivariate reliability tool holder (IMRTH) during wear and corrosion resistant applications.
Conclusions
- Desired requirements of materials, treatments and part surface properties, qualities and reliability can be determined with the help of integrated multivariate reliability sensor-based selection device, instead of using subjective selection methods.
- Each wear coating has different characteristics of strength, shrinkage, hardness, and other qualities, such that there is a material for every wear resistant category.
- As the hardness of material increases, so is the wear resistance.
- These coatings and treatments fall under the following three categories:
– Soft Coatings or Solid Film Lubricants (treatment provides low strength and low friction to provide wear resistance)
– Surface Treatments (treatments increase the surface hardness and provide wear resistance)
– Hard Surface Replacement Coatings – Hard Surfacing (the wear behavior is only a function of the coating and not the base material.
- Hard Surfacing category can easily be controlled by an engineering technique (e.g model-based – welding, thermal spray, technological inheritance techniques and others) to achieve a maximum reliability.
- The two general uses for hard surfacing are that, it can be applied to repair worn surfaces, and can be applied to obtain more desirable surface properties.
- The advantages of hard surfacing are the greater the thickness available the better it is to achieve maximum quality and reliability.
- Cost-effective selection of the required wear resistance parameters, treatments and design of part surfaces (spindle and bearings) is possible with IMRSSD.
References
- Reference
- 1. Osarenren J.O, (2012) “Integrated Reliability: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance of Equipment”, CRC Press, Florida, 479p.













Leave a Reply